Let’s learn how to create a custom form in Drupal 9. If you know already how to create a custom form in Drupal 8 there is not much different, it’s almost the same.
First, you need to create a custom module to create a form. To create a custom module in Drupal 9 is something similar to Drupal 8.
1) Creating a module in Drupal 9
Go to your drupal path and create a folder called ‘my_custom_form’: /drupal9/module/custom/my_custom_form
then, create a file info.yml file
i) my_custom_form.info.yml
name: 'my_custom_form' type: module description: 'Custom form using a custom module' core: 8.x package: 'Custom' core_version_requirement: '^8 || ^9'
So the only difference from Drupal 8 in the info.yml is ‘core_version_requirement‘. Without this line, the custom module will not work in Drupal 9.
2) Creating a form
The second step is to create a custom form, for that’ we need a routing file, so let’s create one
Go to the path: /drupal8/module/custom/my_custom_form and create a route file:
ii) my_custom_form.routing.yml
my_custom_form.my_form:
path: '/myform'
defaults:
_form: '\Drupal\my_custom_form\Form\MyForm'
_title: 'MyForm'
requirements:
_access: 'TRUE'
As you can see there is no difference from Drupal 8. Drupal 9 routing.yml is the same as Drupal 8.
After creating the above file, create two folders src and Form inside my_custom_form, So the structure would look like this now,
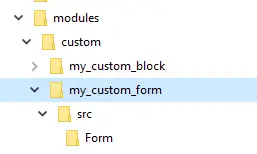
Inside the ‘Form’ folder create a PHP Class and put the below code:
iii) MyForm.php
<?php
namespace Drupal\my_custom_form\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Class MyForm.
*/
class MyForm extends FormBase {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getFormId() {
return 'my_form';
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form['name'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Name'),
'#description' => $this->t('Enter your fullname'),
'#maxlength' => 64,
'#size' => 64,
'#weight' => '0',
];
$form['phone'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Phone'),
'#description' => $this->t('Enter your phone number'),
'#maxlength' => 64,
'#size' => 64,
'#weight' => '0',
];
$form['email'] = [
'#type' => 'email',
'#title' => $this->t('Email'),
'#description' => $this->t('Enter your email'),
'#weight' => '0',
];
$form['submit'] = [
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => $this->t('Submit'),
];
return $form;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function validateForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
parent::validateForm($form, $form_state);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
// Display result.
foreach ($form_state->getValues() as $key => $value) {
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage($key . ': ' . $value);
}
}
}
Just go through the above code, to create a form, you need to extend “FormBase” which is the core class and the form interface.
Again the only difference in the above code is instead of drupal_set_message() (which is deprecated in Drupal 9), I have used \Drupal::messenger()->addMessage().
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
When you use FormStateInterface, you should use the following functions as well getFormId(), buildForm(), and submitForm() without these functions a form cannot be created.
getFormId() – this is where you have to mention your form id and it should be unique
buildForm() – this is where you will create your form
validateForm() – here you can write your form validations
submitForm() – this is where you can handle submit processes
Now you have your custom module and a custom Form created, go to “Extends” and enable the module and then access the route path.
https://localhost/drupal/myform to see your custom form
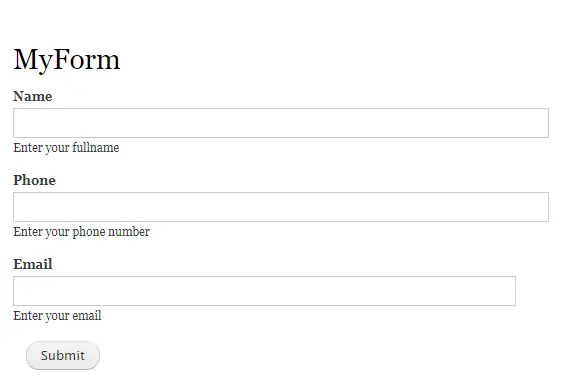
You can download this Drupal 9 custom module with a form in my GitHub page,

